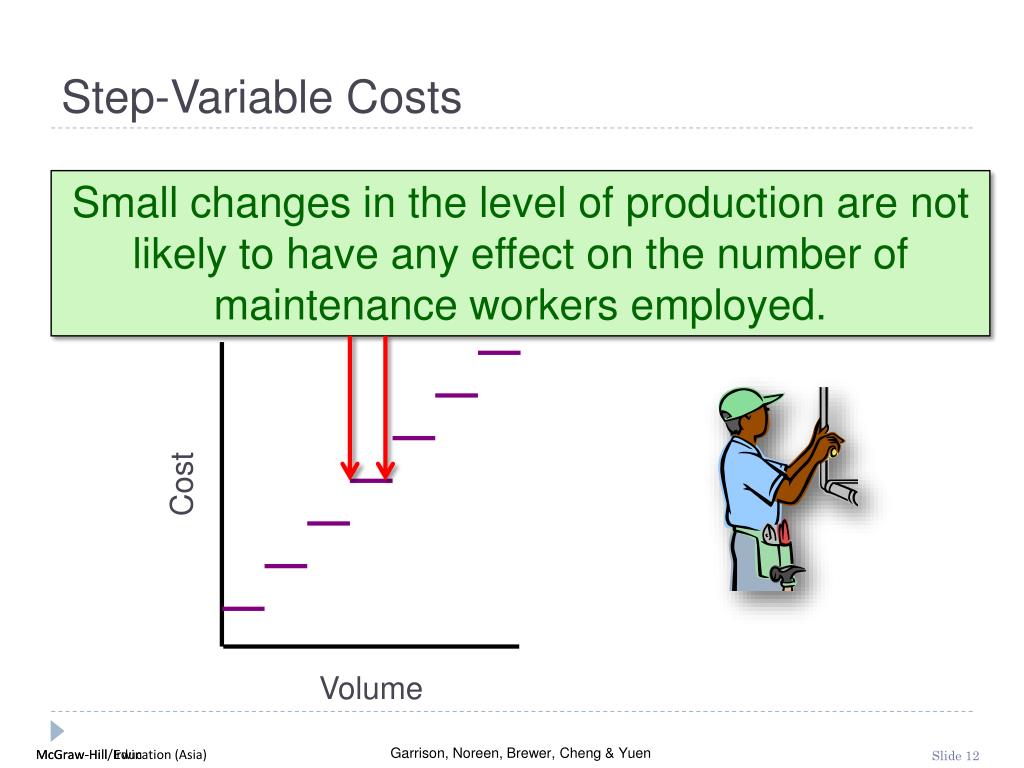
If demand rises to 1,050 units, the company might create an additional production shift to manufacture more units. The step cost incurred would be the salaries as the company would pay additional salaries for shift supervisors to oversee the additional shift. This example mentions the cost relating to various activity levels (i.e., units produced).
What does stepped cost mean?
A step cost is a cost that does not change steadily with changes in activity volume, but rather at discrete points. The concept is used when making investment decisions and deciding whether to accept additional customer orders. A step cost is a fixed cost within certain boundaries, outside of which it will change. The same pattern applies in reverse when the volume of activity declines. As you have learned, much of the power of managerial accounting is its ability to break costs down into the smallest possible trackable unit. In many cases, businesses have a need to further refine their overhead costs and will track indirect labor and indirect materials.
Effects of Changes in Activity Level on Unit Costs and Total Costs
For instance, a manager may need cost information to plan for the coming year or to make decisions about expanding or discontinuing a product or service. In practice, the classification of costs changes as the use of the cost data changes. In fact, a single cost, such as rent, may be classified by one company as a fixed cost, by another company as a committed cost, and by even another company as a period cost. Understanding different cost classifications and how certain costs can be used in different ways is critical to managerial accounting. Semi-variable Costs Semi-variable costs are costs that have both a variable and fixed component.
Understanding Step Costs
As these costs vary directly in proportion to the level of production, they would not be incurred in situations where production level is zero. The article “true variable vs step variable cost” looks at meaning of and differences between these two types of variable costs – true variable cost and step variable cost. If you look at your business finances, you’ll discover that many of your expenses are examples of step costs.
Cost Accounting Helps Reduce Fraud and Promotes Ethical Behavior
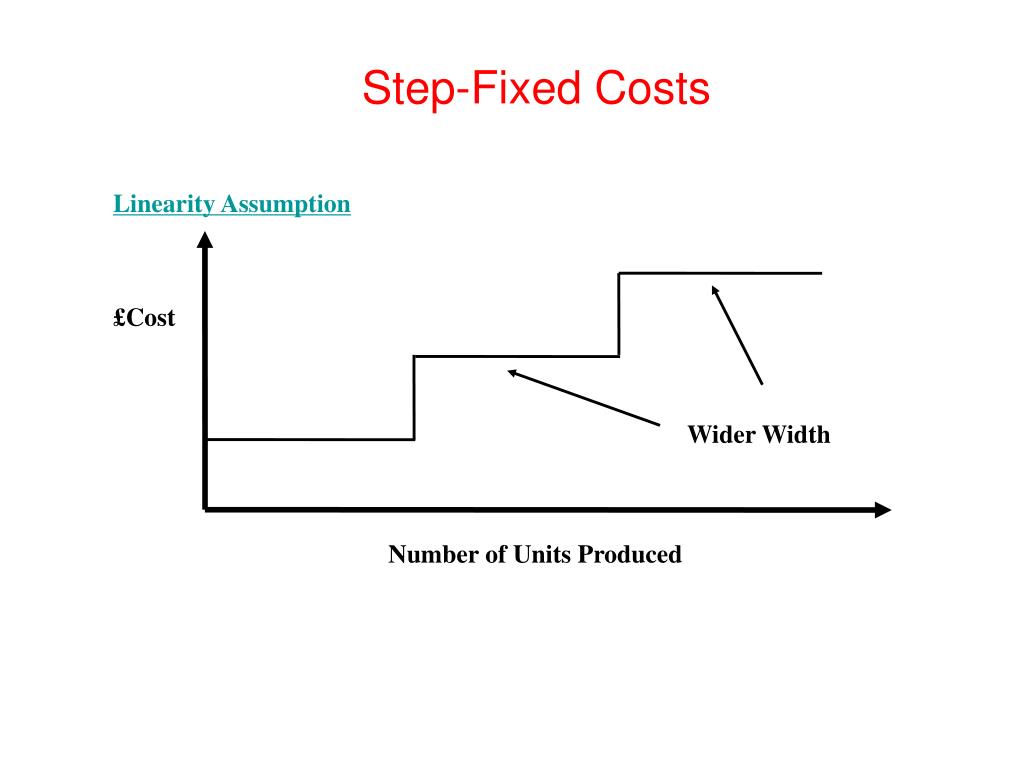
However, once that level is breached, step cost graph increases or decreases in a step-like fashion. Fixed costs are those costs that don’t change regardless of the amount produced. If our pencil maker hires a bookkeeper for $10,000, this is a fixed cost because the cost stays the same regardless of the number of pencils that are produced. For example, if a processing facility capacity why would a vendor request a w9 form purpose behind the need is 100,000 units of production, 100,000 is the upper limit of the range for the fixed cost. Production over 100,000 will require additional facility investment which will mean more fixed costs. This understanding and analysis of cost behavior is of great importance for management to take decisions regarding production and other activities that may have a core impact on cost.
If the company hires a second quality inspector, they would be stepping up their fixed costs. In effect, they will double the relevant range to allow for a maximum of 160 inspections per shift, assuming the second QA inspector can inspect an additional 80 units per shift. The down side to this approach is that once the new QA inspector is hired, if demand falls again, the company will be incurring fixed costs that are unnecessary. For this reason, adding salaried personnel to address a short-term increase in demand is not a decision most businesses make.
Health care and pension contributions can also fluctuate when staffing levels rise or fall below a certain threshold. To return to the example, this means that the QA person could be more efficient or work somewhat longer hours in order to avoid incurring the large incremental cost of an additional person. In such a situation, it may be more cost-effective for the employer to offer overtime to the existing staff than to pay the more substantial cost of a new hire. Discretionary fixed costs generally are fixed costs that can be incurred during some periods and postponed during other periods but which cannot normally be eliminated permanently.
- As long as management understands when these costs will be incurred, it can plan operations to avoid them for as long as possible, thereby maintaining the highest possible level of profits.
- The term step-variable costs is a synonym for semi-variable or semi-fixed costs and contemplates an increase in costs with an increase in capacity.
- Variable cost is one key categorization of total costs incurred in a business unit.
- They remain fixed per unit of production but change in total based on the level of activity within the business.
- Tony operates a screen-printing company, specializing in custom T-shirts.
When the visits are in the range of 1,000 to 2,999 the monthly cost jumps to $50. As the data indicates, the total monthly cost is constant or fixed only for a given range of activity (number of visits). When the number of visits exceeds the upper limit of a range, the monthly cost jumps to a higher level and remains fixed until the visits exceed the new upper limit. When opening a new production facility, business owners will need to consider the additional step costs in employee salaries and equipment.
Step cost, also known as a step-variable cost or a step-fixed cost, is a type of cost that exhibits a sudden and discrete change in value at specific activity levels or production thresholds. Unlike variable costs that change proportionally with changes in activity, step costs remain constant within a certain range of activity and then “step up” to a higher level when that range is exceeded. In each of the examples, managers are able to trace the cost of the materials directly to a specific unit (cake, car, or chair) produced. Since the amount of direct materials required will change based on the number of units produced, direct materials are almost always classified as a variable cost.
These overhead costs are not directly attributable to a specific unit of production, but they are incurred to support the production of goods. Some of the items included in manufacturing overhead include supervisor salaries, depreciation on the factory, maintenance, insurance, and utilities. It is important to note that manufacturing overhead does not include any of the selling or administrative functions of a business. It requires the application of labor to the raw materials and component parts.
